Snapshots in Neuroscience: Mossy fiber boutons
These images have been selected to showcase the art that neuroscience research can create.
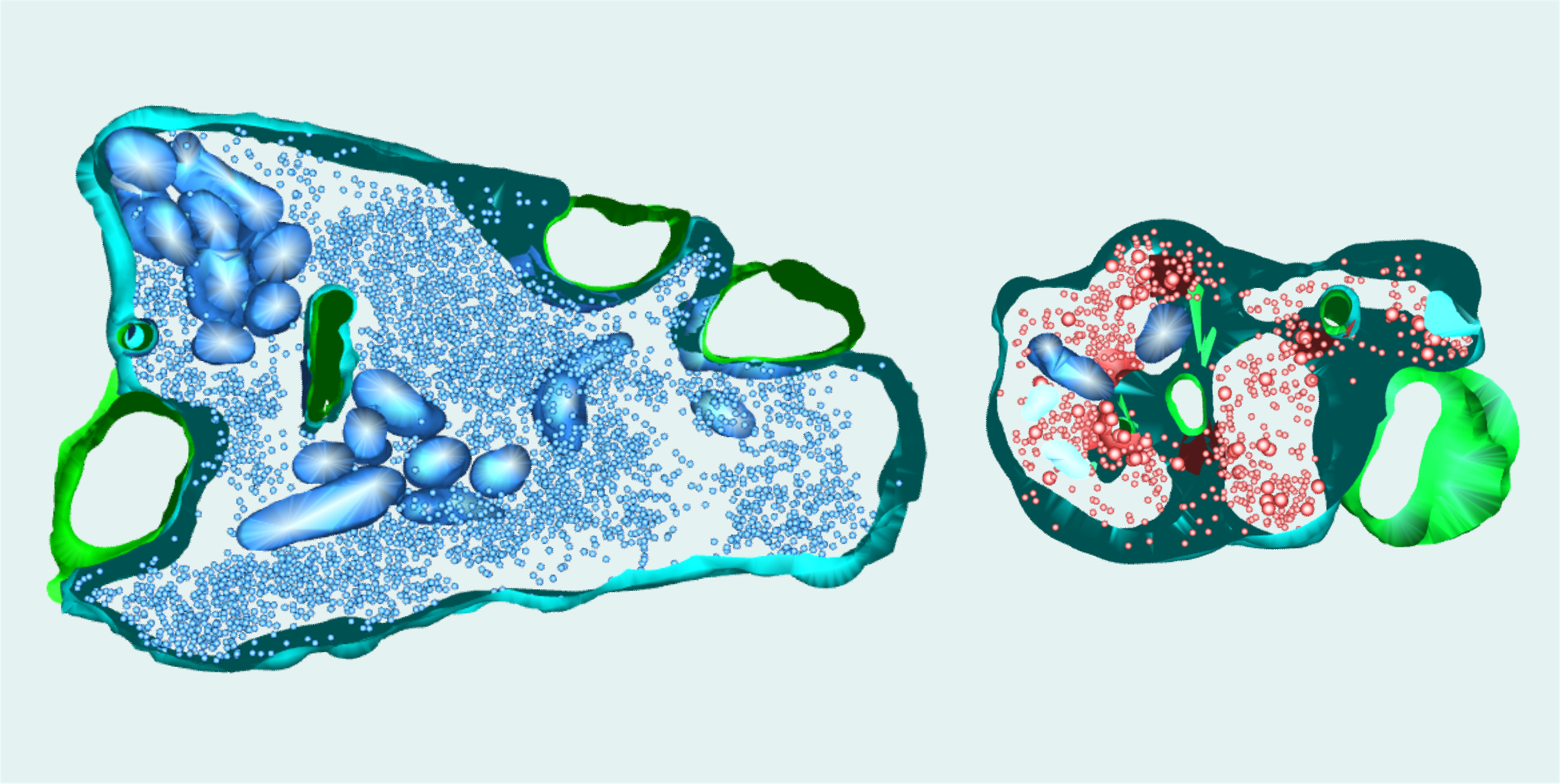
As described by Dr. Marta Orlando and colleagues: “This image displays partial 3D reconstructions of mossy fiber boutons, which are unique synapses in the hippocampus. The presynaptic membrane is shown in turquoise, the postsynaptic membrane in green. Inside the presynaptic compartment, synaptic vesicles can be detected as small spherical structures (blue and red, respectively). The synapse on the left is from a wild-type mouse; the synapse on the right is from a mouse lacking the synaptic protein synapsin (synapsin knock-out). Synapsin regulates the clustering of synaptic vesicles and thereby also their availability for release.
“This image highlights some of the structural changes in mossy fiber synapses occurring upon the loss of all synapsin isoforms: Synapses from the knock-out model contain fewer but more dispersed vesicles than wild-type synapses. We found that these changes, together with an increase in active zone density, underlie disturbed presynaptic plasticity patterns in the knock-out model. Pronounced forms of presynaptic plasticity are a hallmark of mossy fiber synapses and the synapsin knock-out model enabled us to shed light on the underlying mechanisms.
“Synapses were partially reconstructed from serial images obtained with a transmission electron microscope operated at 80 kV and equipped with a digital camera. Mossy fiber synapses were imaged in chemically fixed hippocampal slices with a 20,000x magnification. Synaptic structures were manually segmented in each image. Stacks contained up to ten images of 70 nm thin serial sections.”
Read the full article:
The Lack of Synapsin Alters Presynaptic Plasticity at Hippocampal Mossy Fibers in Male Mice
Felicitas Bruentgens, Laura Moreno Velasquez, Alexander Stumpf, Daniel Parthier, Jörg Breustedt, Fabio Benfenati, Dragomir Milovanovic, Dietmar Schmitz, and Marta Orlando
FOLLOW US
POPULAR POSTS
TAGS
CATEGORIES


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed




