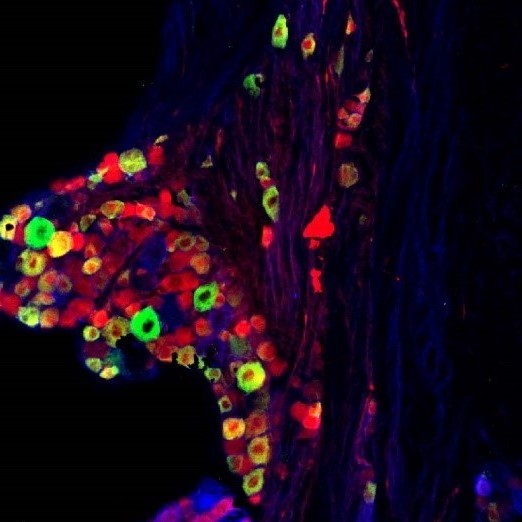
Heterogeneity of neuronal cell bodies of sensory nerves within the vagal ganglia.
Authors examined the reliability of using Cre-induced recombination of one gene to predict recombination in another gene at the single-cell level in adult hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells.
Alexandra Castillo-Ruiz and Nancy Forger tell the story about their eNeuro paper that sheds light on the long-standing question of what controls the timing and magnitude of developmental neuronal cell death.
Authors explored the role of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis in the reinstatement and renewal of fear—two forms of fear relapse that are differentially triggered by stress.
See the most-shared articles of March/April 2020; Volume 7, Issue 2
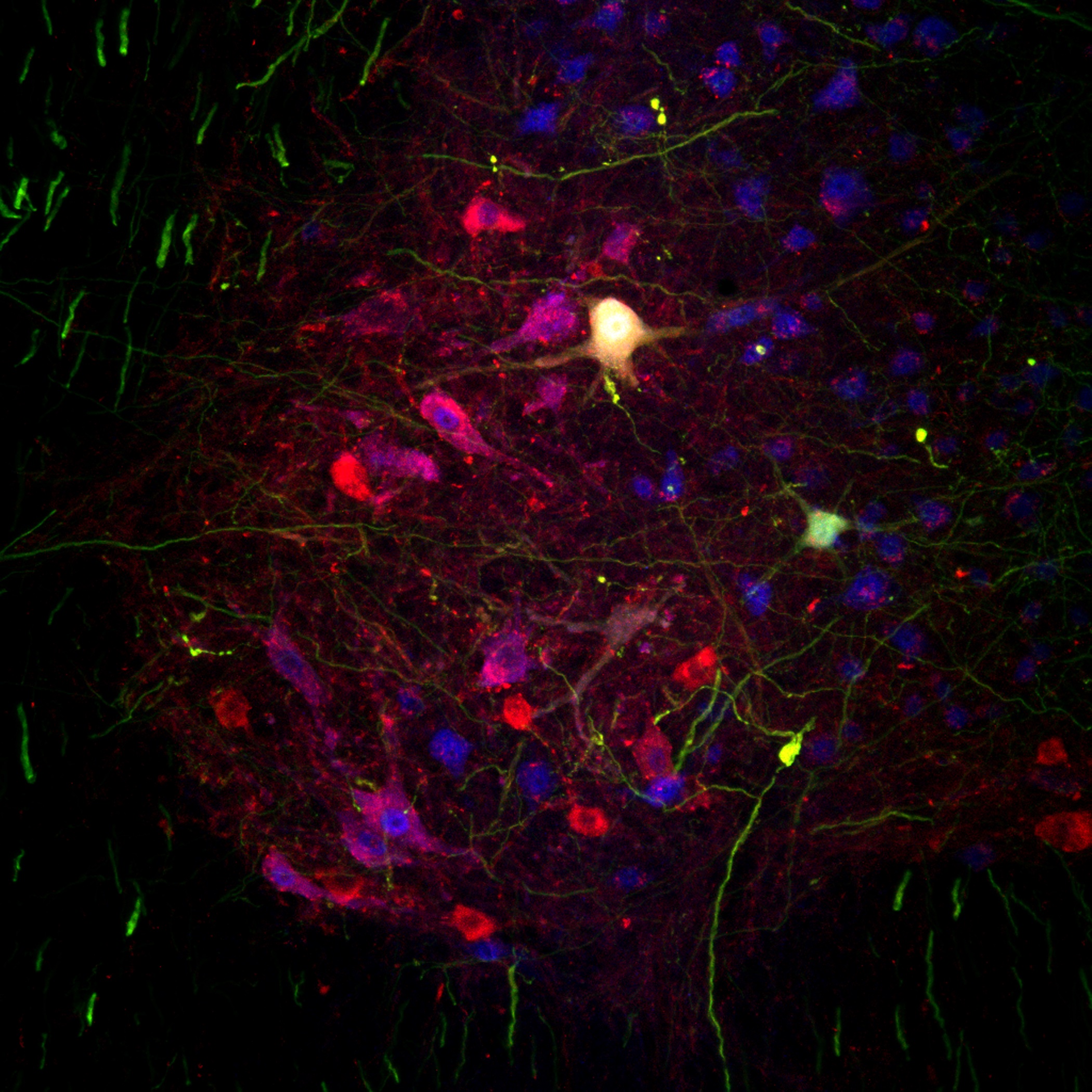
Motor Neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord of an ALS mouse model.
Chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal in rats produce opposing effects on glutamate release in the basolateral amygdala from axons originating in subdivisions of the medial prefrontal cortex, chemogenetic inhibition attenuates the increase in anxiety-like behavior associated with ethanol withdrawal.
Authors demonstrate that ApoE deficiency and the ApoE4 human isoform both impair hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice and give insight into how ApoE may influence hippocampal-related neurological diseases.
Omri Nachmani and Gunnar Blohm talk about their paper on how sensorimotor prediction and uncertainty modulate oculomotor tracking behavior, and share their thoughts on publishing through the Registered Report format.
Synaptic boutons in the muscle of a larval fruit fly
FOLLOW US
TAGS
CATEGORIES





.jpg)
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed




